Six Plastic Bottle Material You Need to Know
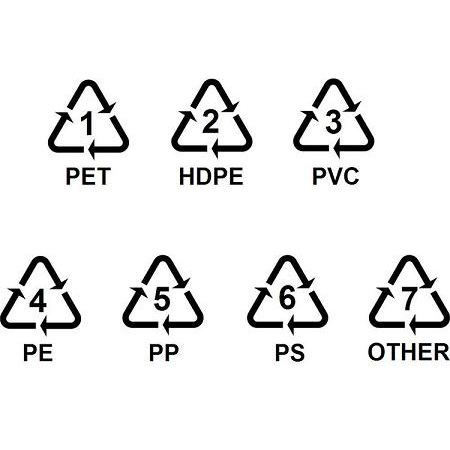 1,PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate)
1,PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate)
is a type of plastic commonly used in the manufacturing of beverage bottles, known as PET bottles.
Features:
- It is characterized by its transparency and the presence of a circular mark at the bottom of the bottle, indicating that it is made in one piece without seams. Initially used for synthetic fibers and materials like film and tape, PET was adopted for beverage bottles in 1976.
- PET bottles are known for their excellent hardness, flexibility, light weight (only 1/9 to 1/15 the weight of glass bottles), ease of transport and use, low energy consumption during production, impermeability to gas, non-volatility, and acid resistance, making them ideal for carbonated drinks, tea, juice, packaged drinking water, alcohol, soy sauce, and other products.
- They are also increasingly used for packaging detergents, shampoo, cooking oil, condiments, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics.
- PET’s heat resistance ranges from about 60°C to 85°C.
Recycled products:
Recycled PET bottles are cleaned, crushed, and re-polymerized into PET chips, which can then be spun into synthetic fibers for use in products such as eco-friendly bags (made from five 1,250cc PET bottles), doll hair, zippers, or transformed into sheets or recycled PET granules for manufacturing various plastic products.
2, Polyethylene (PE)
is broadly categorized into High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) and Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE), known for its wide industrial and household applications.
Features:
- HDPE, with a higher melting point, offers greater hardness and resistance to corrosive liquids, making it suitable for packaging dairy products, detergents, and cooking oils.
- LDPE is ubiquitous in modern life, primarily used for plastic bags and films due to its prevalence and adaptability. The heat resistance of HDPE ranges from 90°C to 110°C, while LDPE ranges from 70°C to 90°C.
Recycled products:
Recycled PE, transformed into plastic granules after being crushed, cleaned, and dried, can be remolded into various products like trash bins and toolboxes, showcasing its versatility in reusability.
3,Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
known for its early invention and widespread use in industrial products, exhibits qualities like other plastics but stands out for its excellent workability and affordability.
Features:
- Although commonly used for non-food items such as pipes and raincoats, PVC’s use in food containers has declined due to health concerns related to the release of Vinyl Chloride Monomer (VCM).
- With a heat resistance between 60°C to 80°C, recycled PVC can be processed into a variety of products, including floor mats and pipes, highlighting the material’s adaptability and ongoing utility in various sectors.
4, Polypropylene (PP)
is akin to its sibling, Polyethylene (PE), yet it surpasses PE in various physical and mechanical properties, leading manufacturers to often use PE for the body of bottles while opting for the harder and stronger PP for caps and handles.
Features:
- PP’s melting point reaches up to 167°C, highlighting its heat resistance and suitability for sterilization. It is primarily used in the production of soy milk and rice milk bottles, as well as containers for 100% pure fruit juices, yogurt drinks, dairy products like pudding, and more.
- Larger items such as buckets, trash bins, laundry tubs, storage baskets, and bins are also commonly made from PP.
- In recent years, PP has been extensively used for disposable tableware and cups, especially for take-out beverages. These PP containers are either opaque or translucent, known for their acid resistance, chemical durability, and impact resistance, withstanding temperatures between 100°C to 130°C.
Recycled products:
Recycled PP, after being crushed, washed, and dried into plastic flakes, can be melted and extruded to produce recycled granules. These granules are then used to manufacture a variety of plastic products, including trash bins, flower pots, appliance casings, stationery, handles for tools, and other elastic plastic recycled products.
5,Polystyrene (PS)
is categorized into two types based on whether it has undergone a foaming process: expanded (EPS) and non-expanded PS. Non-expanded PS is mainly used in construction materials, toys, stationery, and also as containers for fermented dairy products like yogurt and cheese.
In recent years, it has been increasingly used for disposable tableware such as cups, salad containers, and egg trays. PS, commonly known as Styrofoam, is created by incorporating a blowing agent to foam the material 20 to 100 times its original volume.
Features:
- This type of PS is utilized for packaging electronic devices or food products like ice cream due to its cushioning and thermal insulation properties.
- Expanded PS is also used for disposable tableware, initially produced as flat sheets (Expanded Polystyrene Paper, PSP) before being molded into various containers. Some food-grade EPS is specifically designed for food containers like coffee cups and jelly cups.
- PS has a relatively low heat resistance of about 70°C to 90°C, making it unsuitable for hot water or oily foods, as well as alcoholic or citrus beverages due to potential health risks.
Recycled products:
Recycled PS, obtained from crushing, washing, and drying the material, can be remelted and extruded into recycled granules. These granules are then used to produce a variety of plastic products such as flower pots, stationery, appliance casings, and other rigid, brittle items that lack elasticity.
6,PLA (PolyLactic Acid)
Identification Features: Transparent, similar appearance to PET containers, difficult to distinguish. PLA is entirely derived from plant starches such as corn, beet, wheat, and sweet potato, through processes of fermentation, dehydration, and polymerization, showcasing its low carbon footprint and energy-efficient advantages.
Features:
- Initially developed for medical applications such as surgical sutures and bone pins, its linear polymer structure has limitations in heat resistance and material strength. However, these can be enhanced by blending with other high-molecular-weight plastic materials to meet the mechanical properties required by certain products.
- Suitable processing methods include vacuum forming, injection molding, blow molding, transparent films, laminating films, cling films, and paper lamination.
- Currently, PLA is used in a variety of products including plastic cups, hot and cold plates, floral packaging, and textile fibers. PLA’s heat resistance is approximately 50°C.
Recycled products:
Recycling and Recycled Products: Due to its similarity in appearance to other traditional plastics, PLA poses challenges in recycling. If correctly sorted post-recycling, it can be processed into plastic flakes, melted, extruded, and then spun into recycled polyester granules. Under controlled conditions, these can be used to produce nursery pots, plant pots, cup holders, and other bioplastic products.